greenhouse effect Understanding Global Change
Table Of Content

All plants — from giant trees to tiny phytoplankton in the ocean — take in carbon dioxide and give off oxygen. He was unable to persuade other parties to back his minority government in Scotland's regional parliament. When those objects release this heat, it doesn't all get out through the windows. Some is reflected back in — the heat radiated by the seats is a different wavelength than the light of the sun that made it through the windows in the first place, and the window glass won't let as much of that wavelength through. "If cirrus clouds behave like a blanket around the Earth, you're trying to get rid of that blanket," Lohmann, a professor of experimental atmospheric physics at ETH Zurich, told Live Science.
Every bite of burger boosts harmful greenhouse gases: UN Environment Agency
Other greenhouse gases like methane and nitrous oxide are increasing as well. The quantity of greenhouse gases is increasing as fossil fuels are burned, releasing the gases and other air pollutants into the atmosphere. Greenhouse gases also make their way to the atmosphere from other sources. The greenhouse effect occurs when greenhouse gases in a planet's atmosphere insulate the planet from losing heat to space, raising its surface temperature.
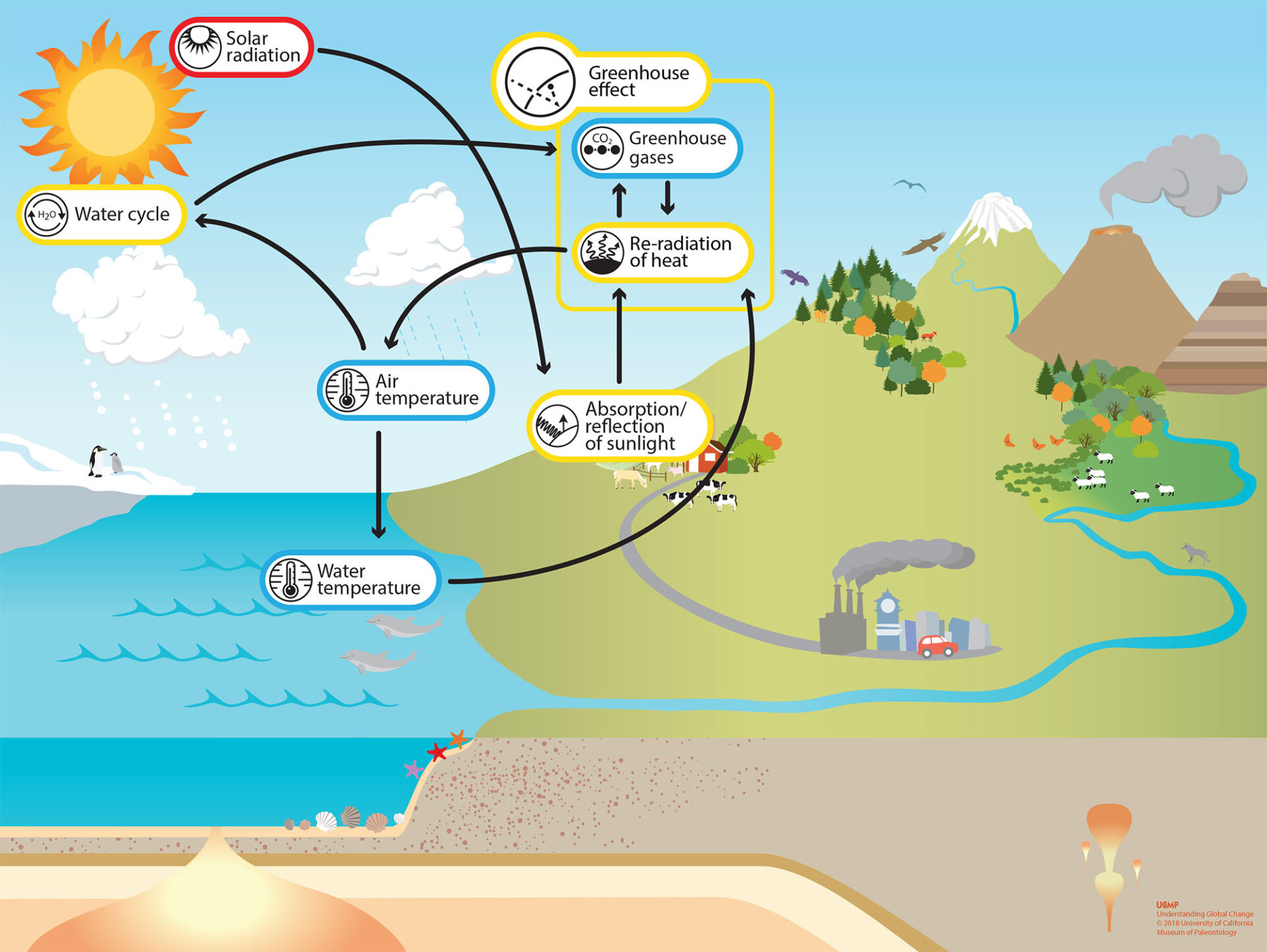
Causes of Greenhouse Effect
The good news is that we have the ability to rein in greenhouse gas emissions – by overhauling our energy systems, habits and lifestyles. The rest of the Sun's energy (20%) is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, like carbon dioxide, water vapor, and methane. Greenhouse effect, a warming of Earth’s surface and troposphere (the lowest layer of the atmosphere) caused by the presence of water vapour, carbon dioxide, methane, and certain other gases in the air. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. Since the middle of the 20th century, greenhouse gases produced by humans have become the most significant driver of climate change, according to the U.S. Carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere have increased by more than 40% since the start of the Industrial Revolution, from roughly 280 parts per million (ppm) to more than 400 ppm today.
More Greenhouse Gases = A Warmer Earth
Click the image on the left to open the Understanding Global Change Infographic. Locate the greenhouse effect icon and identify other topics that cause changes to, or are affected by, the greenhouse effect. After a few hundred or thousand years, Mars might actually have an environment that humans could simply walk around in — all thanks to the greenhouse effect. So, a certain amount of energy is going in, and less energy is going out. There's a delicate balancing act occurring every day all across the Earth, involving the radiation the planet receives from space and the radiation that's reflected back out to space. By making choices that have less harmful effects on the environment, everyone can be a part of the solution and influence change.
Greenhouse Gases
The Woman Who Demonstrated the Greenhouse Effect - Scientific American
The Woman Who Demonstrated the Greenhouse Effect.
Posted: Thu, 09 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
For example, theories published in the journal Science in July 2017 by lrike Lohmann and Blaž Gasparini, researchers at the Institute of Atmospheric and Climate Science at ETH Zurich in Switzerland, proposed reducing cirrus clouds that trap heat. Greenhouses work well to offer a good habitat for growing plants because they let the visible light in but trap the residual heat. However, trapping too much heat can be dangerous, the single most important example of this being global climate change. Scientists attribute the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century to the human expansion of the "greenhouse effect"1 — warming that results when the atmosphere traps heat radiating from Earth toward space.
What are greenhouse gas emissions?

Ocean acidification is making it hard for some sea creatures to build shells and skeletal structures. This could alter the ecological balance in the oceans and cause problems for fishing and tourism industries. This phenomenon occurs when the planet absorbs more radiation than it can radiate back. Thus, the heat lost from the earth’s surface is less and the temperature of the planet keeps rising. Scientists believe that this phenomenon took place on the surface of Venus billions of years ago.
Emission temperature and altitude
For example, thawing permafrost releases methane, and wildfires increase carbon dioxide levels. We can learn a lot about climate change from our sister planet Venus, Earth’s nearest neighbour. Venus currently has a surface temperature of 450 °C (hot enough to turn lead to liquid, NASA scientists say) and an atmosphere dominated by 96 % carbon dioxide – making it a burning inferno. Although fluorinated gases are emitted in smaller quantities than other greenhouse gases (they account for 3 percent of U.S. emissions, per the EPA), they trap substantially more heat.
Greenhouse gases in the atmosphere also absorb and hold some of the heat energy radiating back from Earth's surface. Introductory video of greenhouse gases, how they are observed, and why they are important. We must protect our carbon-storing forests and reduce food waste and the emissions that go with it. We should be doubling down on reducing emissions from dirty power plants and cars and trucks. And as individuals, we must commit to taking carbon-cutting actions in our daily lives. This temperature increase has long-term, adverse effects on the climate, and affects a myriad of natural systems.
Atmosphere
Effects include increases in the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events – including flooding, droughts, wildfires and hurricanes – that affect millions of people and cause trillions in economic losses. Studies show that solar variability has played a role in past climate changes. For example, a decrease in solar activity coupled with increased volcanic activity helped trigger the Little Ice Age. Human activities are driving the global warming trend observed since the mid-20th century. Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are the only greenhouse gases not created by nature.
While the radiative forcing due to greenhouse gases may be determined to a reasonably high degree of accuracy... The uncertainties relating to aerosol radiative forcings remain large, and rely to a large extent on the estimates from global modeling studies that are difficult to verify at the present time. Unfortunately, the increased carbon dioxide in the ocean changes the water, making it more acidic. Let us have a look at the greenhouse gases and understand the causes and consequences of greenhouse effects with the help of a diagram. A thick, low cloud cover can enhance the reflectivity of the atmosphere, reducing the amount of solar radiation reaching Earth’s surface, but clouds high in the atmosphere can intensify the greenhouse effect by re-radiating heat from the Earth’s surface.
EPA estimates that the 60 Solar for All recipients will enable over 900,000 households in low-income and disadvantaged communities to deploy and benefit from distributed solar energy. This $7 billion investment will generate over $350 million in annual savings on electric bills for overburdened households. The program will reduce 30 million metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent emissions cumulatively, from over four gigawatts of solar energy capacity unlocked for low-income communities over five years. Solar and distributed energy resources help improve electric grid reliability and climate resilience, which is especially important in disadvantaged communities that have long been underserved. Incoming UV radiation easily passes through the glass walls of a greenhouse and is absorbed by the plants and hard surfaces inside. Weaker IR radiation, however, has difficulty passing through the glass walls and is trapped inside, thus warming the greenhouse.
Comments
Post a Comment